Understanding Share Premium Accounts: Uses and Examples
This disclosure provides investors and analysts with a clear view of the additional capital the company has raised, which can be a significant indicator of financial health and market perception. Understanding share premium accounts is crucial for grasping how companies manage and report these extra funds. This financial mechanism not share capital and share premium only impacts corporate balance sheets but also influences broader financing strategies and shareholder equity structures. In conclusion, the differences between a share premium account and share capital account lie in their composition, repayment, and usage. Share capital represents the capital that shareholders have invested in the company, while share premium is the amount investors pay above the face value of shares.
- The strategic utilization of share premium reserves is a critical aspect of financial management that can significantly influence a company’s growth trajectory.
- The treatment of share premium is not uniform across the globe, and international accounting standards play a pivotal role in ensuring consistency and transparency.
- Both share capital and reserves are subject to legal and regulatory requirements, which vary depending on the jurisdiction and the type of company.
- There are various ways to create a capital reserve, and each method has its unique advantages and disadvantages.
Share buybacks reduce the number of outstanding shares, which increases earnings per share and improves the company’s valuation. Dividends provide a return on investment for shareholders and can attract new investors to the company. Assume that ABC Company issued 1,000 shares of stock for subscription to the public. The company assigned the shares a par value of $10 each, expecting to raise a share capital of $10,000. A share premium account is sometimes referred to as an additional paid-in account, and it is included in the shareholder’s equity section of a balance sheet.
The Evolving Role of Share Premium in Business Finance
The Share Premium Account can be used as an indicator of a company’s financial health, management practices, and risk profile. It is a valuable tool for investors and analysts to assess the company’s prospects and make informed decisions. As such, it is important for companies to maintain a strong share premium and manage it effectively to ensure long-term growth and success. The face value of each share is $10, so the total face value of the shares is $10,000. However, the total amount of money that the company raises from the sale of the shares is $50,000.
It is also an indicator of a company’s financial position and can increase shareholder value. Companies should pay attention to their Share Premium Account and use it wisely to improve their financial performance. In some cases, companies may choose to cancel their share premium account and transfer the money to their capital reserve.
While the share premium is a valuable financial tool for companies, it carries inherent challenges and risks that require careful management and strategic foresight. Balancing the expectations of various stakeholders and navigating the regulatory and market landscapes are crucial for maintaining the value derived from share premiums. Investors, on the other hand, scrutinize share premiums as part of their risk assessment. A premium that’s too high might indicate an overvalued company, while a too-low premium could point to undervaluation or a lack of confidence by existing shareholders.
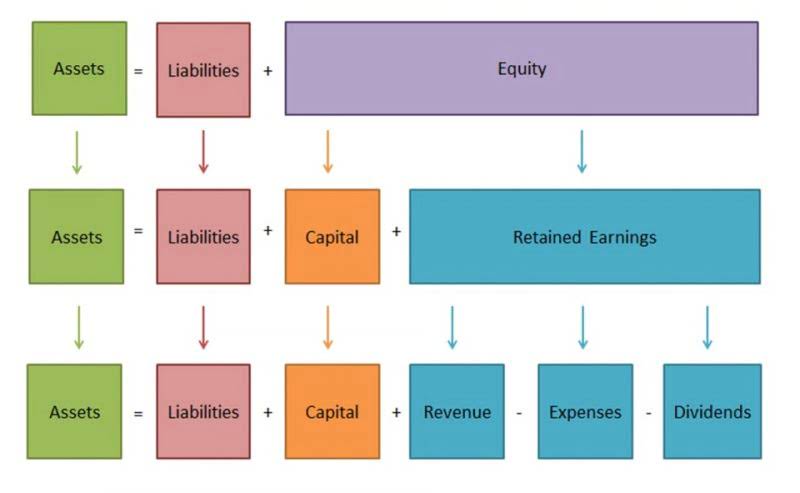
- Share capital and reserves are fundamental components of a company’s equity, representing the funds contributed by shareholders and the accumulated profits retained in the business.
- For the company, it’s a strategic reserve that can be used for beneficial investments or improving the company’s financial health.
- This account forms part of shareholders’ equity and is subject to specific legal restrictions regarding its use.
From regulatory compliance to market volatility, managing a share premium account demands strategic foresight and meticulous oversight. From the perspective of corporate governance, the creation of a share premium account is a strategic move. It’s a declaration that the company values prudent financial management and is committed to safeguarding shareholder interests.
Example of Share Capital and Reserves
Understanding the accounting treatment of share premium account is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and making informed decisions. The share premium account is a crucial aspect for publicly listed companies, and the accounting treatment of the same must be accurately recorded and reported in the financial statements. It is important for all stakeholders to understand the nuances of the share premium account to make informed investment decisions. If a company incurs losses, it cannot use the funds in these accounts to cover them. Capital reserves and share premium account are two critical financial metrics that companies need to understand and manage effectively.
Share Premium: Maximizing Value: The Role of Share Premium in Paid in Capital
The par value is the lowest price at which the shares can be issued to the general public. But premium is the amount of money that the investors are ready to pay willingly pay to the company beyond the nominal value of the issued shares. Other than the use of two accounts to record the separate elements of the price at which a share is sold, there is no particular relevance to the concept of a premium. This occurs because companies typically issue new shares based on current market value, not the arbitrary par value.
As a result, the company records $5,000 to the common stock account and $45,000 to the paid-in capital in excess of par. Both of these accounts added together equal the total amount stockholders were willing to pay for their shares. Preferred sharessometimes have par values that are more than marginal, but most common shares today have par values of just a few pennies. The ending balance of the Share Premium account is recorded in the Statement of Financial position after the Share Capital. Issuing shares at a premium is a commonly used practice as par value is often set at a minimum level and does not reflect the true worth of the company.
For example, consider a tech startup that has shown promising growth and innovation in its sector. Investors might value the shares at $$ 50 $$, even though the nominal value is only $$ 10 $$. The $$ 40 $$ difference per share would go into the Share Premium Account, reflecting the market’s belief in the company’s potential beyond its current financials. The share premium account can also be used for the payment of dividends on preference shares. However, this can only be done if the articles of association of the company permit it. Capital reserves are typically created using profits that a company has earned over a certain period.
Share premium is the additional amount of funds received exceeding the par value of security. A company issues its shares at a premium when the price at which it sells the shares is higher than their par value. This is quite common, since the par value is typically set at a minimal value, such as $0.01 per share. A company can use the balance of the account only for purposes that have been established in its bylaws.
It’s not merely a financial metric; it encapsulates the collective sentiment of investors about the company’s potential for growth and profitability. One crucial aspect, especially for a company limited by guarantee, is the impact on share price and valuation. When shares are issued at a premium, it often indicates confidence in the company’s future growth and profitability. As a result, investors may interpret this as a positive signal, leading to increased demand for the company’s shares in the market.
Share premium can be a useful tool for companies to raise additional capital and strengthen their balance sheet. However, companies need to consider the advantages and disadvantages before using it and should compare it with other financing options to choose the best option for their business. According to International financial Reporting standards (IFRS), share premium is recognized as part of equity.